Time:2025-03-05 Views:1
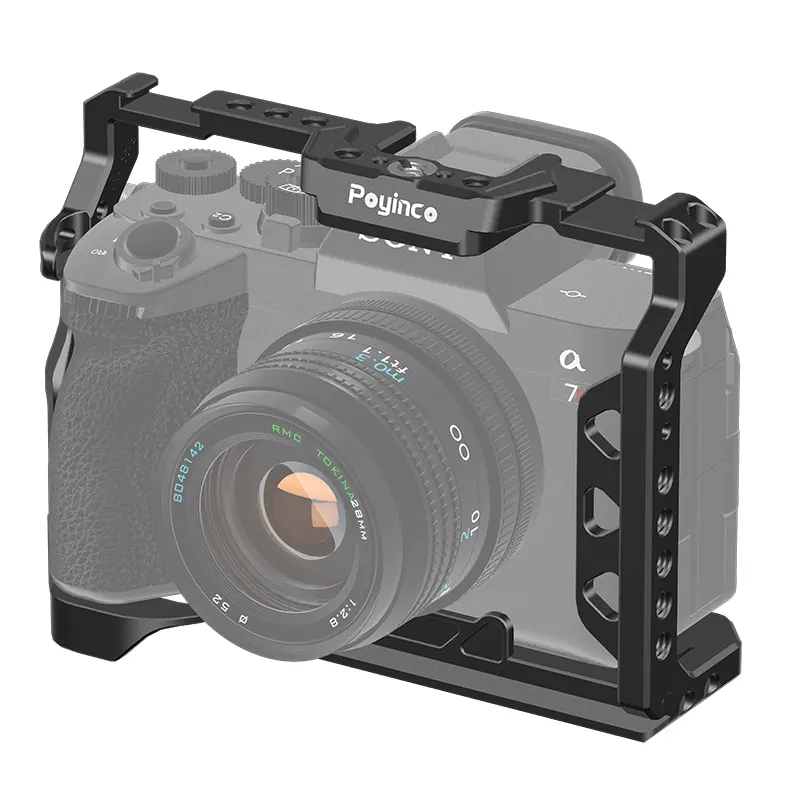

Quick - release plates are crucial components in various mechanical and industrial systems, and their aging resistance is of great significance for long - term reliable operation.
Material - related Aging Factors
The materials used in the manufacture of quick - release plates play a fundamental role in determining their aging resistance. For example, if a plate is made of common carbon steel, it is highly susceptible to corrosion over time. Exposure to moisture, oxygen, and various environmental chemicals can initiate a series of electrochemical reactions on the steel surface. Rust will gradually form, which not only reduces the aesthetic appearance but also weakens the mechanical properties of the plate. In contrast, plates made of stainless steel, especially those with a high chromium and nickel content, are much more resistant to corrosion. The chromium in stainless steel forms a passive oxide layer on the surface, which acts as a barrier against further oxidation and corrosion. Another important material aspect is the polymer materials used in some quick - release plates for specific functions, such as insulation or shock - absorption. Polymers can age due to factors like ultraviolet (UV) radiation, heat, and chemical exposure. UV radiation can break the chemical bonds in polymers, leading to chain scission and a reduction in mechanical strength. For instance, polypropylene - based components in quick - release plates may become brittle and lose their flexibility after long - term exposure to sunlight.
Mechanical Stress - induced Aging
During normal use, quick - release plates are subjected to repeated mechanical stress. Each time the plate is engaged and disengaged, there are forces acting on its structure. This cyclic loading can cause fatigue in the material. Micro - cracks may initiate at stress - concentration points, such as corners or holes in the plate. Over time, these micro - cracks can grow and eventually lead to the failure of the plate. The rate of fatigue - induced aging can be affected by the magnitude of the stress, the frequency of loading, and the material's fatigue resistance. High - strength alloys with good fatigue resistance are often preferred for quick - release plates in applications where they are frequently used. Additionally, improper installation or misalignment can also increase the mechanical stress on the plate, accelerating the aging process. If the plate is not properly fastened or is under uneven loading, it will experience additional stress, which can lead to premature wear and aging.
Environmental Conditions and Aging
The environmental conditions in which quick - release plates are used also have a significant impact on their aging resistance. In high - humidity environments, the risk of corrosion for metal - based plates is greatly increased. Salt - laden air, such as in coastal areas, is particularly corrosive. The presence of salt ions in the air can accelerate the electrochemical corrosion process. In industrial settings with high levels of chemical pollutants, the plates may be exposed to acids, alkalis, or other corrosive substances. These chemicals can react with the plate material, causing degradation. For example, aluminum - alloy quick - release plates may be attacked by strong alkalis, resulting in the dissolution of the metal surface. Temperature also plays a role. Extreme high or low temperatures can affect the material properties. High temperatures can soften some materials, reducing their strength, while low temperatures can make materials more brittle, increasing the risk of cracking.
Read recommendations: